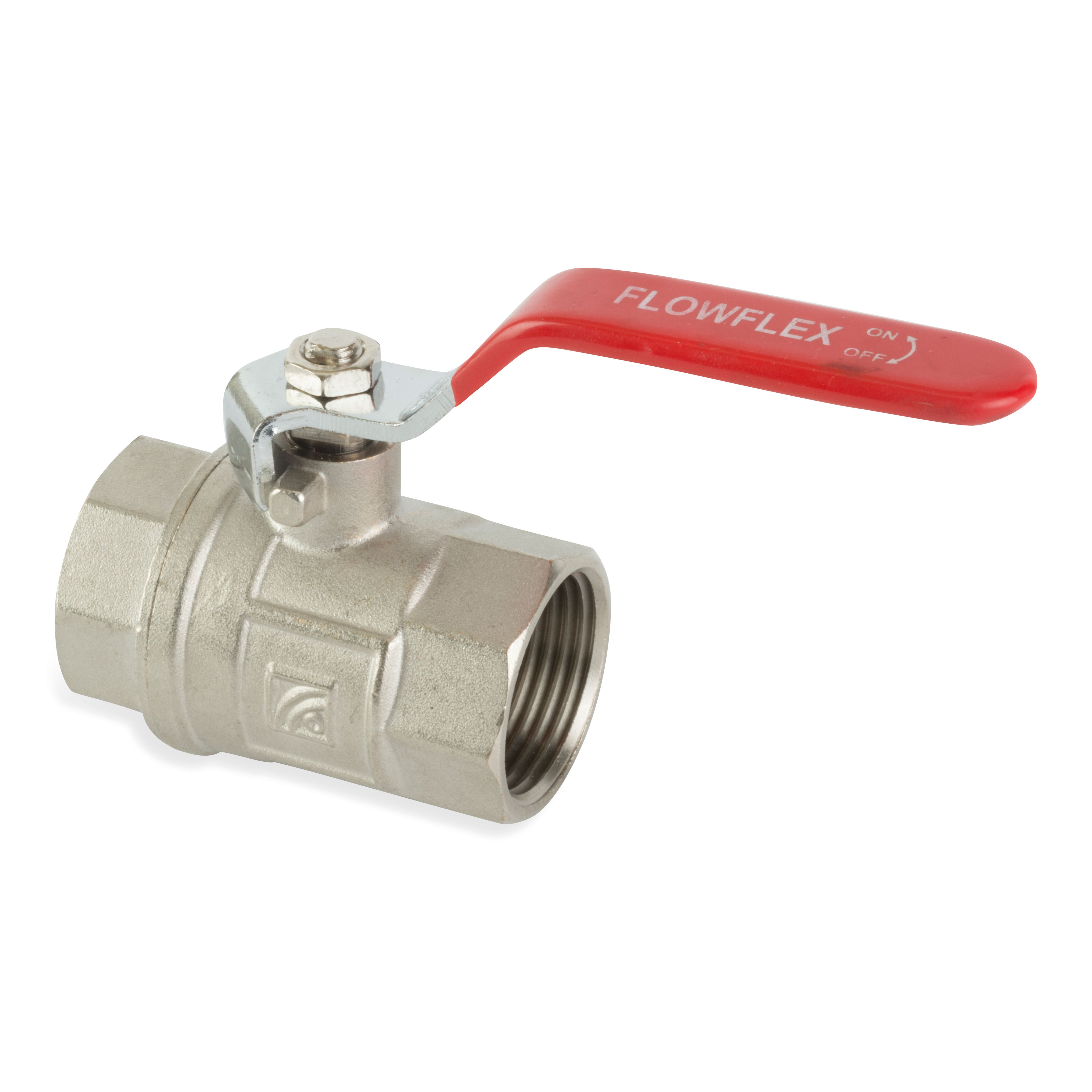
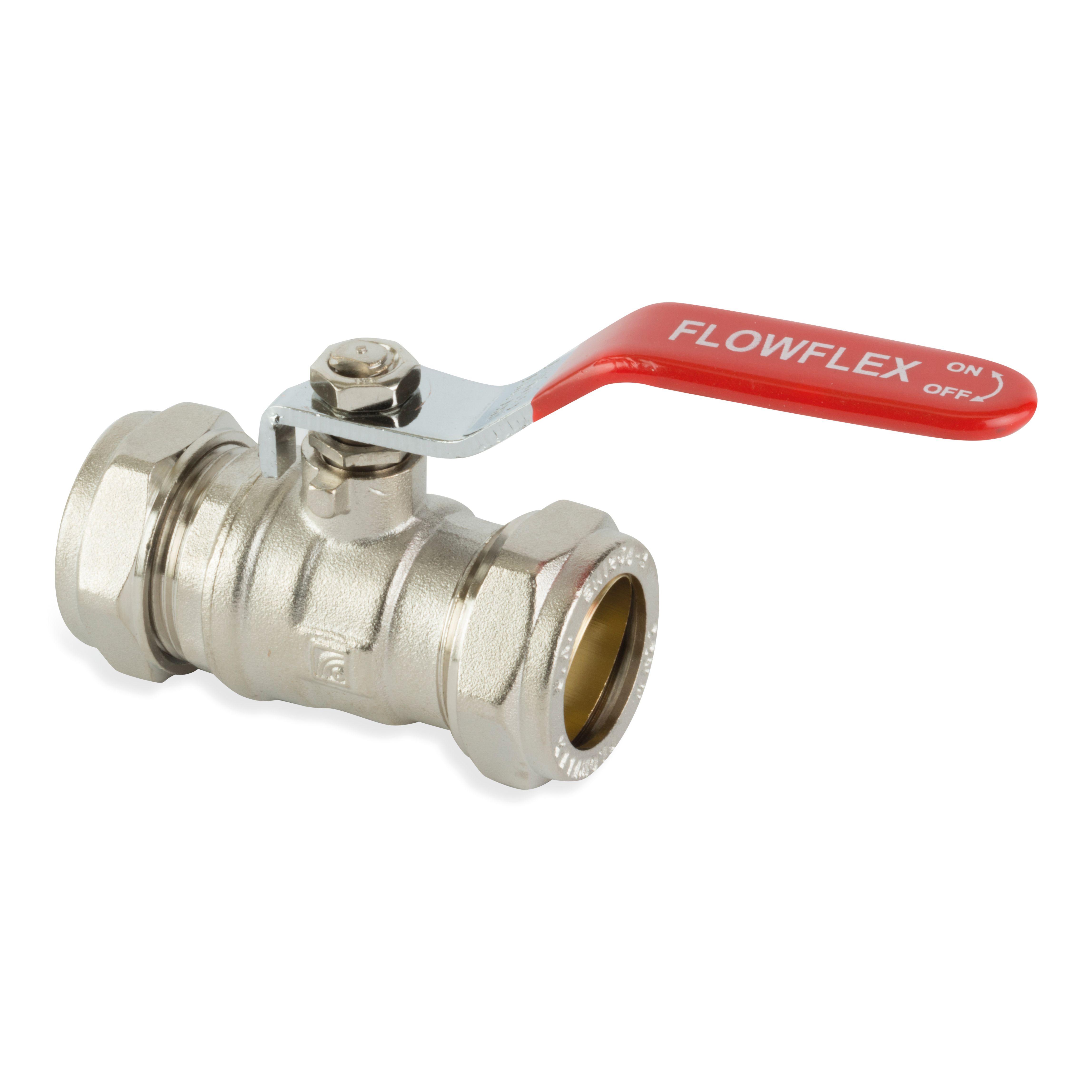
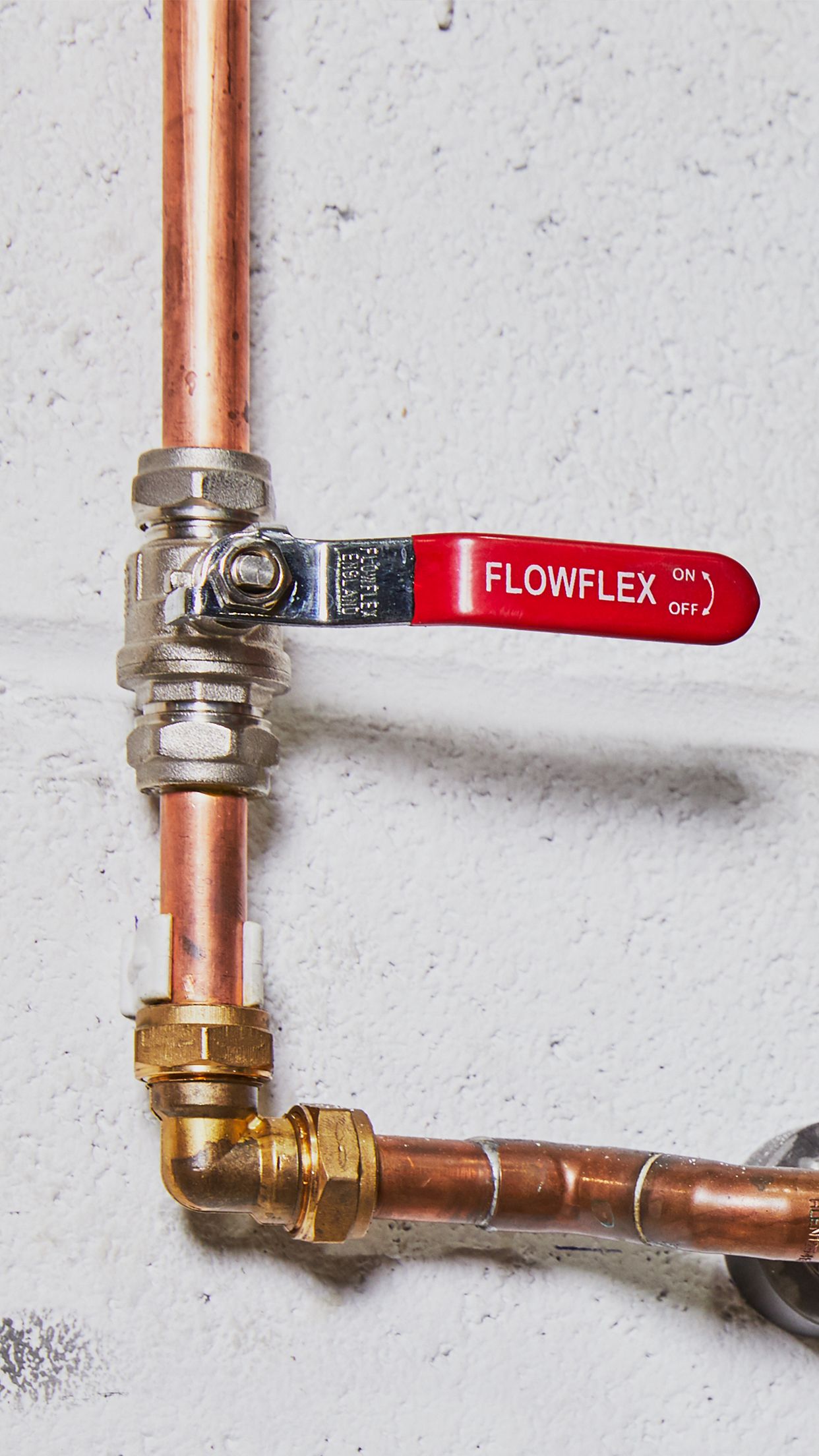
Flowflex Ball Valves are a quick way of isolating flow in a system. Flow is controlled through a quarter turn action which moves the hole in the ball inline or out of line with the flow, preventing or facilitating flow as appropriate.
Brass Ball Valves are regarded as a long term and reliable solution, performing well after long periods of disuse. The quick operation of a Ball Valve, is an advantage, and makes it ideal for emergency applications, however by the same merit, a disadvantage may be that Ball Valves induce water hammer in a system.
Applications
- Domestic
- Commercial
- Industrial